

- PROXYMAN WEBSOCKET HOW TO
- PROXYMAN WEBSOCKET UPGRADE
- PROXYMAN WEBSOCKET CODE
It’s an essential concept every developer has to learn: Parse data from JSON and display it in your UI. It validates the value in the header X-SECRET-KEY at initial handshake.It’s almost impossible to write apps these days without using some kind of networking.
PROXYMAN WEBSOCKET CODE
The sample code implements a similar concept. For example, Amazon API Gateway provides the option to require API clients to pass the API key as the X-API-Key header. A commonly used method for simple authentication is to set the relevant ticket in the HTTP header.
PROXYMAN WEBSOCKET HOW TO
There are several options for where and how to tell the "ticket" from the client to the server. See Authorization and IPs chapter in Armin Ronacher's post Websockets 101 for detail.
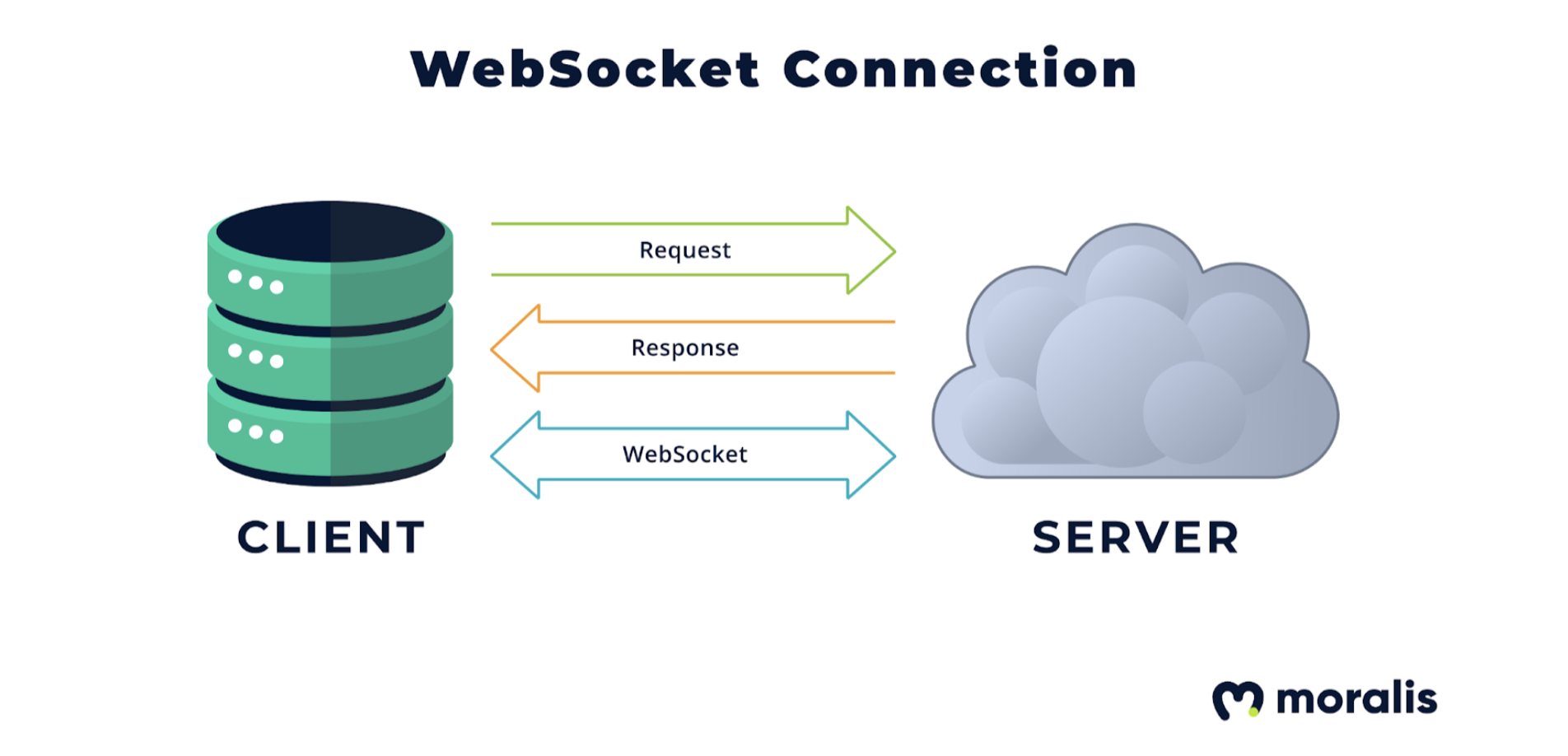
The server can compare this ticket, check an user's condition (i.e. The client opens the WebSocket connection, and sends along this "ticket" as part of an initial handshake. The server stores the ticket and returns it to the client. The client-side contacts the server-side to obtain an authorization "ticket". There are several patterns to implement authentication, and Heroku Dev Center - WebSocket Security describes one pattern - "ticket" -based authentication system. However, it is a problem that anyone can access the WebSocket server without authentication just because the protocol is not prepared.īusiness requirements often require authenticating the connecting WebSocket client and associating it with a registered customer record. The WebSocket protocol does not handle authorization or authentication. The following diagram, quoted by Wikipedia, describe a communication using WebSocket between client and server. The first step is to start up a WebSocket server which waits for requests from WebSocket clients.Īs a side note, WebSocket is a mechanism for low-cost, full-duplex communication on Web, which protocol was standardized as RFC 6455. Relay TCP connection in WebSocket data to "internal API". Relay TCP connection from "App" to the peer of WebSocket. I will explain the rest points in part 2 and beyond. The following points to implement this design will be explained in this post. In this design, it starts with a request for a WebSocket connection from wsp client to wsp server. Therefore, the starting point is wsp client in the internal network. For example, if the client is launched on your local PC, it is not possible to send a request to the client from an external server. The internal network restricts incoming requests from outside or does not have any global IPs, so that it is not possible for external server to connect to a client started in an internal network. Here is a terminal image when sending a HTTP request from app. However, maintenance has stopped since the days of Go 1.6, so I'll proceed with this post based on code hgsgtk/wsp that I forked and modified for the Go situation in 2021 (Thank you root-gg).Įnter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode It is difficult to use in production, but it is a good learning material to explain the design of reverse proxy over WebSocket. wsp is developed by root-gg, which is a reverse HTTP proxy over WebSocket, whose aim is to securely make call to internal APIs from outside. In this post, we will focus on understanding the basic concepts and read prototypical and simpler one root-gg/wsp. 
In Go, inconshreveable/ngrok and coyove/goflyway is well known, especially ngrok is popular among developers as a SaaS service.
In JavaScript, mhzed/wstunnel is well known, in Haskell, erebe/wstunnel is. There are not that many examples of implementation reverse proxy over WebSocket. It is a type of proxy server that retrieves resources on behalf of a client from servers.įurther, this post focuses on a reverse HTTP proxy over WebSocket, in brief, it uses the WebSocket protocol as a "tunnel" to pass TCP communication from server to client.

In contract, a reverse proxy is the opposite of what a forward proxy does. It allow users to hide their IP address while accessing a Web service or an API server. There are two types of proxies, forward proxy and reverse proxy.Ī forward proxy (or gateway, or tunnel, or just "proxy") provides proxy services to a client or a group of clients.
Authentication of WebSocket is a difficult design problem, and there are many options. PROXYMAN WEBSOCKET UPGRADE
To achieve compatibility with HTTP, the WebSocket handshake uses the HTTP Upgrade header in order to change from the HTTP protocol to the WebSocket protocol.
WebSocket is designed to work over HTTP. In Go project, gorilla/websocket is widely used to implement WebSocket. A reverse HTTP proxy over WebSocket is a type of proxy server which uses the WebSocket protocol as a "tunnel" to pass TCP communication from server to client.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
